All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
- – Review Of Cannabidiol - Canada.ca in Clovis-Cal...
- – Dimtris Tree Felling Biz: Call now for a quote
- – Dimtris Tree Felling Biz: Call now for a quote
- – Cannabidiol - Mercy in St.-Petersburg-Florida
- – Dimtris Tree Felling Biz: Call now for a quote
- – Investigators Testing Cbd As Treatment For Par...
- – Dimtris Tree Felling Biz: Call now for a quote
- – Safety And Side Effects Of Cannabidiol, A Can...
- – Dimtris Tree Felling Biz: Call now for a quote
Review Of Cannabidiol - Canada.ca in Clovis-California
Dimtris Tree Felling Biz: Call now for a quote
111 Cedar St # 12, Austin, TX 9918300 333 1200 993
Click here to learn more
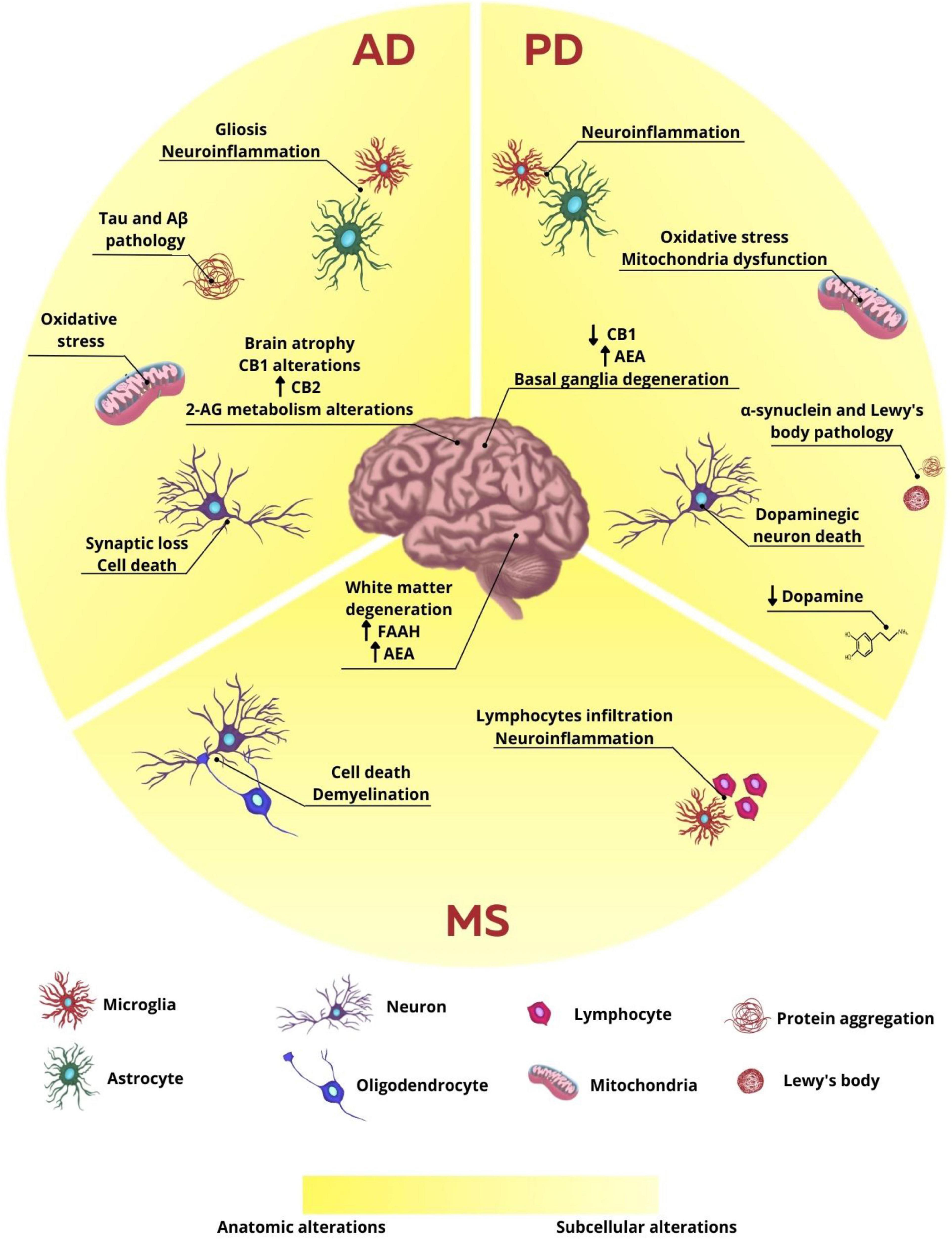
Celorrio M, Fernandez-Suarez D, Rojo-Bustamante E, Echeverry-Alzate V, Ramirez MJ, Hillard CJ, et al. Fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibition for the symptomatic relief of Parkinson's disease. Brain Behav Immun. 2016;57:94-105. On the other hand, daily administration of CBD (3 mg/kg) for 14 days decreased both dopamine depletion and tyrosine hydroxylase expression within the striatum of rats that received 6-OHDA.101101.
Cannabinoids provide neuroprotection against 6-hydroxydopamine toxicity in vivo and in vitro: relevance to Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2005;19:96-107. These neuroprotective effects were associated with an upregulation of m, RNA levels of Cu2+/Zn superoxide dismutase, a key enzyme necessary for the endogenous control of oxidative stress. 102102. Garcia-Arencibia M, Gonzalez S, de Lago E, Ramos JA, Mechoulam R, Fernandez-Ruiz J.

Brain Res. 2007;1134:162-70. Beyond these neuroprotective effects, one study suggested a putative antidyskinetic effect of CBD in hemiparkinsonian mice chronically treated with L-DOPA. Of note, although CBD administration does not reduce L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia, when combined with the TRPV1 receptor antagonist capsazepine, a significant antidyskinetic effect was observed (capsazepine alone also failed to decrease dyskinesia).
Dimtris Tree Felling Biz: Call now for a quote
111 Cedar St # 12, Austin, TX 9918300 333 1200 993
Click here to learn more
Dos-Santos-Pereira M, da-Silva CA, Guimaraes FS, Del-Bel E. Co-administration of cannabidiol and capsazepine reduces L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in mice: possible mechanism of action. Neurobiol Dis. 2016;94:179-95. CBD also prevented cataleptic behavior induced by repeated administration of reserpine9191. Santiago AN, Mori MA, Guimaraes FS, Milani H, Weffort de Oliveira RM. Effects of cannabidiol on diabetes outcomes and chronic cerebral hypoperfusion comorbidities in middle-aged rats.
Cannabidiol - Mercy in St.-Petersburg-Florida
2019;35:463-74. or haloperidol. In the latter case, CBD also produced a reduction in c-Fos protein expression in the dorsal striatum via activation of 5-HT1A serotonin receptors. 104104. Sonego AB, Gomes FV, Del Bel EA, Guimaraes FS. Cannabidiol attenuates haloperidol-induced catalepsy and c-Fos protein expression in the dorsolateral striatum via 5-HT1A receptors in mice.
2016;309:22-8.,105105. Gomes FV, Del Bel EA, Guimaraes FS. Cannabidiol attenuates catalepsy induced by distinct pharmacological mechanisms via 5-HT1A receptor activation in mice. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2013;46:43-7. An open-label pilot study conducted in PD patients showed that oral doses of CBD ranging from 150-400 mg/day, combined with classic antiparkinsonian agents, reduced psychotic symptoms evaluated by different scales (the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale [BPRS] and the Parkinson Psychosis Questionnaire [PPQ]) with no influence on cognitive and motor signs and no severe side effects.
Dimtris Tree Felling Biz: Call now for a quote
111 Cedar St # 12, Austin, TX 9918300 333 1200 993
Click here to learn more
Zuardi AW, Crippa JA, Hallak JE, Pinto JP, Chagas MH, Rodrigues GG, et al. Cannabidiol for the treatment of psychosis in Parkinson's disease. J Psychopharmacol. 2009;23:979-83. In a case series with four patients, CBD reduced the frequency of events related to REM sleep behavior disorder. 107107. Chagas MH, Eckeli AL, Zuardi AW, Pena-Pereira MA, Sobreira-Neto MA, Sobreira ET, et al.
J Clin Pharm Ther. 2014;39:564-6. In a subsequent clinical trial, 300 mg/day of CBD improved mobility, emotional well-being, cognition, communication, and body discomfort compared to placebo. The authors suggest that this effect might be related to the anxiolytic, antidepressant, and antipsychotic properties of CBD.108108. Chagas MH, Zuardi AW, Tumas V, Pena-Pereira MA, Sobreira ET, Bergamaschi MM, et al.
Investigators Testing Cbd As Treatment For Parkinson Disease ... in Columbus-Ohio

J Psychopharmacol. 2014;28:1088-98. Since CBD is well tolerated in humans, these positive effects suggest it could be a promising alternative for PD pharmacotherapy. Therefore, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trials with larger samples of patients with PD are needed to elucidate the possible effectiveness and mechanisms involved in the therapeutic potential of CBD in this movement disorder.
Dimtris Tree Felling Biz: Call now for a quote
111 Cedar St # 12, Austin, TX 9918300 333 1200 993
Click here to learn more
Additionally, studies conducted specifically to evaluate the safety profile of CBD in patients with PD (including long-term safety), possible interactions with other antiparkinsonian drugs, and possible side effects, as well as the therapeutic window for motor and non-motor PD symptoms are also required.
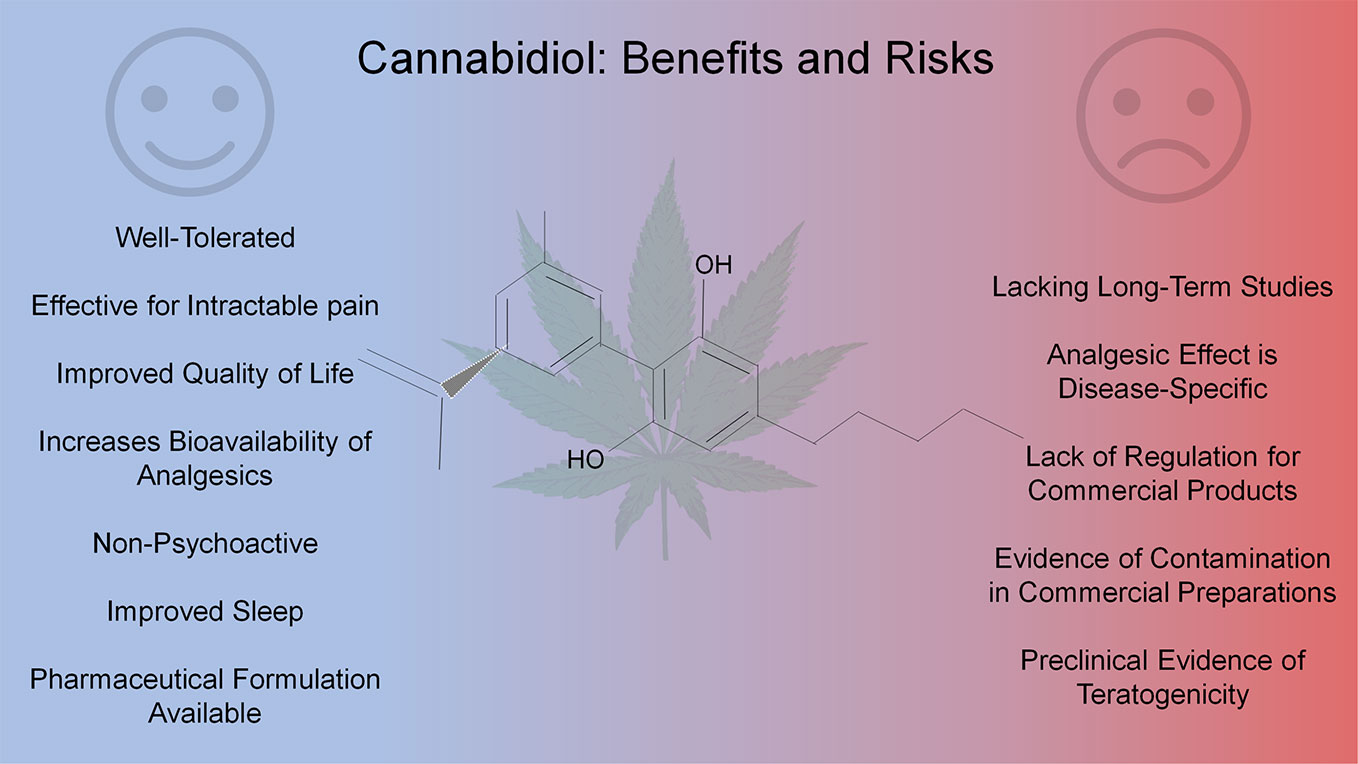
Cannabidiol (CBD) can provide relief for Parkinson’s patients. This was shown in a study by the Department of Neurology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine in Aurora (USA). The motor symptoms of the disease were reduced, but also nighttime sleep and emotional disturbances improved significantly. However, liver enzymes elevated in some participants of the study due to the high dosage.
The CBD extract was titrated from 5 to 20-25 mg per kilogram of body weight and maintained for 10 to 15 days. The patients had an average age of 68 years. All 13 participants in the study reported mild side effects, such as diarrhoea (85%), somnolence (69%), fatigue (62%), weight gain (31%), dizziness (23%), abdominal pain (23%) and headache, weight loss, nausea, anorexia and increased appetite (5% each).
Safety And Side Effects Of Cannabidiol, A Cannabis Sativa ... in Edinburg-Texas
Dimtris Tree Felling Biz: Call now for a quote
111 Cedar St # 12, Austin, TX 9918300 333 1200 993
Click here to learn more
5% of the total group. Three people dropped out of the study due to intolerances. The remaining ten achieved an improvement in overall and motor scores. Other positive results were that nightly sleep and emotional or behavioural control disorders improved significantly. The researchers therefore conclude that CBD in the form of Epidiolex may be effective in PD.
Table of Contents
- – Review Of Cannabidiol - Canada.ca in Clovis-Cal...
- – Dimtris Tree Felling Biz: Call now for a quote
- – Dimtris Tree Felling Biz: Call now for a quote
- – Cannabidiol - Mercy in St.-Petersburg-Florida
- – Dimtris Tree Felling Biz: Call now for a quote
- – Investigators Testing Cbd As Treatment For Par...
- – Dimtris Tree Felling Biz: Call now for a quote
- – Safety And Side Effects Of Cannabidiol, A Can...
- – Dimtris Tree Felling Biz: Call now for a quote
Latest Posts
The Case For The Entourage Effect And Conventional Breeding ... in Muswell Hill, London
6 Facts About Americans And Marijuana - Pew Research Center in Muswell Hill, London
What Is Cbd And How Is It Different From Marijuana? - Quartz in Muswell Hill, London
More
Latest Posts
The Case For The Entourage Effect And Conventional Breeding ... in Muswell Hill, London
6 Facts About Americans And Marijuana - Pew Research Center in Muswell Hill, London
What Is Cbd And How Is It Different From Marijuana? - Quartz in Muswell Hill, London